Wear Scar Characteristics of Thermal Power Plant Waste Reinforced Nickel Matrix Composite Coatings
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.112.1.2131Keywords:
Nickel, fly ash, composite coating, wearAbstract
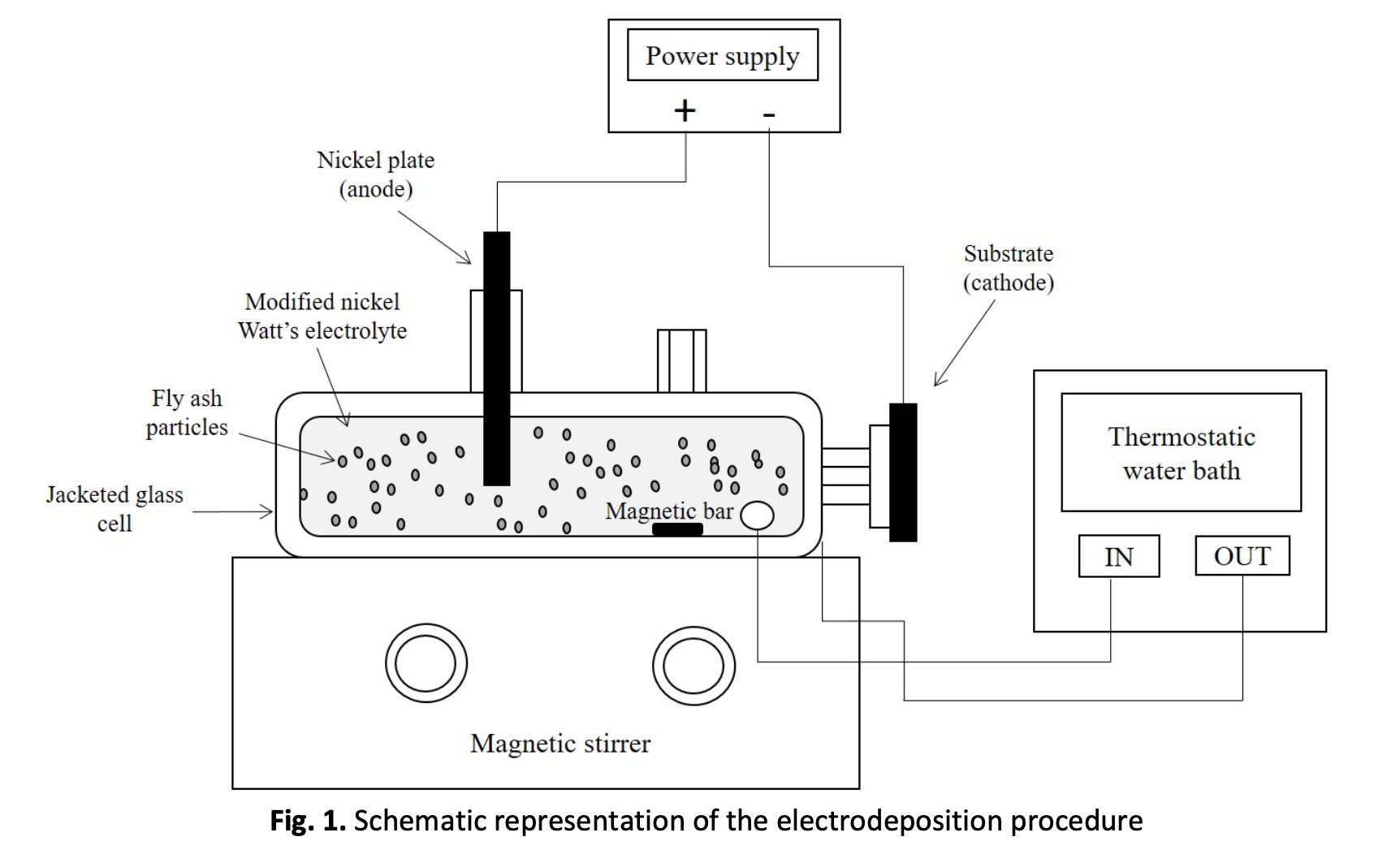
This research delves into the distinct wear scar properties exhibited by pure nickel and nickel composite coatings with varying concentrations of fly ash when sliding against a stainless steel ball on an aluminium alloy 6061 (AA6061) substrate. The composite coatings were formulated from a modified nickel Watt's bath using an electrodeposition technique, involving a 1-hour process at 40°C and a current density of 5 A/dm². Through experimentation utilizing a high-frequency reciprocating rig (HFRR) tester, the resulting composite coatings underwent assessment, capturing the features of the scar surfaces. Notably, the Ni-FA (nickel-fly ash) composite coating, comprising 90 g/l of fly ash, demonstrated notably enhanced wear resistance in contrast to both the pure nickel coating and the Ni-FA composite coatings with lower fly ash concentrations. The disparities in morphology between the pure nickel and Ni-FA composite coatings were discernible through scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and analysis of surface roughness on the wear scars. These distinctions can be attributed to the varying impacts of fly ash concentration on the wear scar characteristics.
Downloads