Response surface methodology of the unsteady axisymmetric magnetic hybrid nanofluid flow subject to a shrinking disk
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.112.1.137148Keywords:
Hybrid nanofluid, response surface analysis, shrinking disk, unsteady flowAbstract
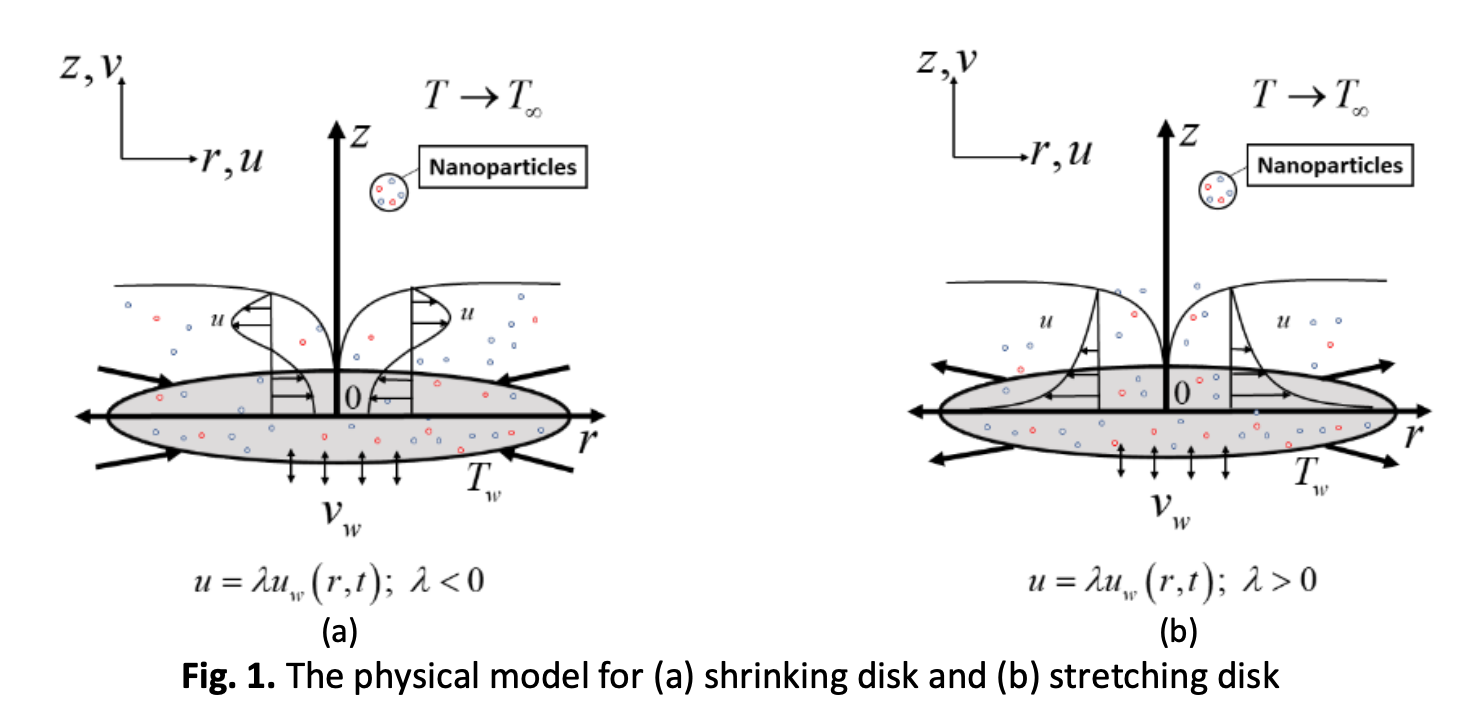
This study examines the unsteady Fe3O4-CoFe2O4/H2O flow over a shrinking disk using both procedures (numerical and statistical). The respective boundary layer model is first transformed into a set of ODEs (ordinary differential equations) using the similarity transformations, and then solved numerically using the bvp4c solver. The duality of solutions is presented within specific use of the parameters such as magnetic field, suction strength and volumetric concentration of hybrid nanoparticles. From the numerical results, the velocity profile increases as the suction and magnetic parameters slightly increase. However, the temperature profile shows a reverse trend as compared to the velocity profile. Meanwhile, the justification of present physical factors (magnetic parameter, suction parameter) whether they are significant or not on the development of responses is tested using the RSM with the fit general linear model in Minitab. In addition, the generated response equation is also beneficial in predicting the flow and thermal distributions of this working fluid for other values of the emerging parameters.
Downloads