Nanoparticle Shape Effects of Aligned Magnetohydrodynamics Mixed Convection Flow of Jeffrey Hybrid Nanofluid over a Stretching Vertical Plate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.112.1.88101Keywords:
Jeffrey hybrid nanofluid, Mixed convection flow, Stretching vertical plate, Nanoparticle shape effect, MagnetohydrodynamicAbstract
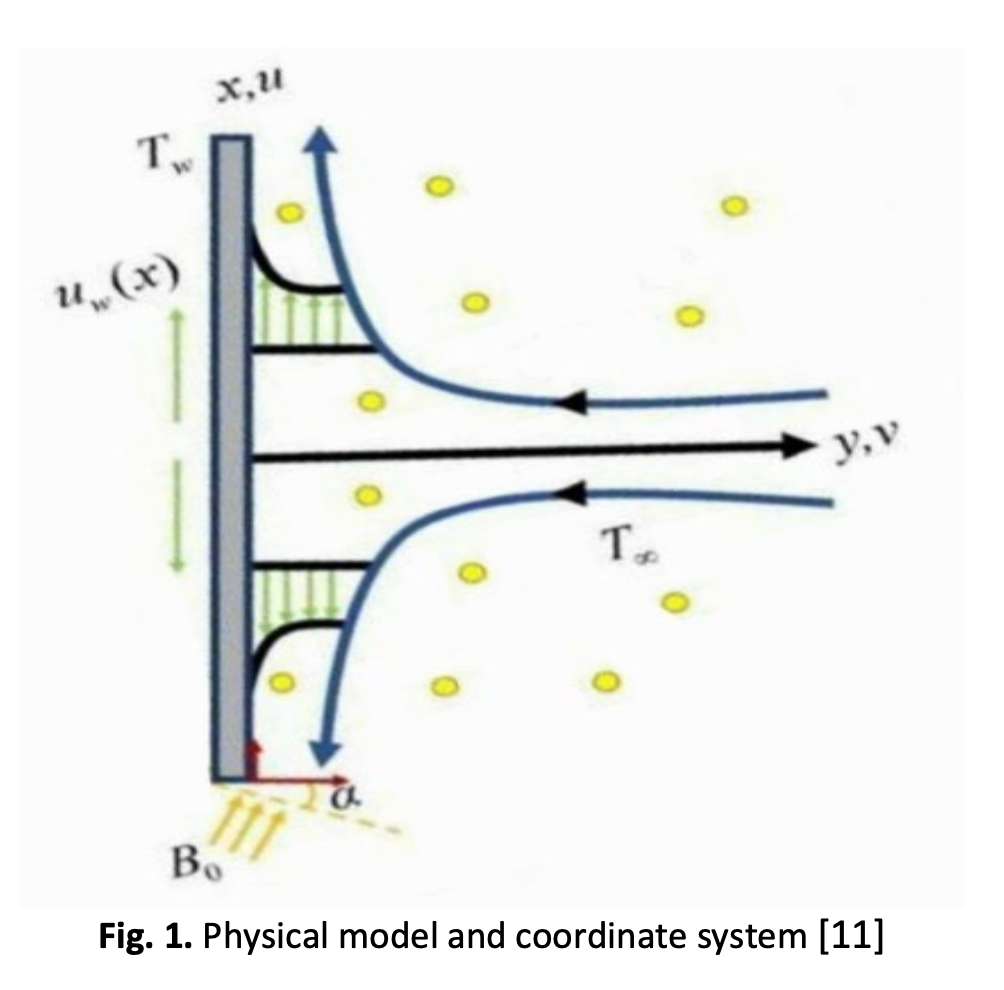
This study investigates the nanoparticle shape effects of aligned magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) mixed convection flow of Cu-Al2O3/water-EG Jeffrey hybrid nanofluid over a stretching vertical plate. Five different shapes of nanoparticles which are spherical, cylindrical, blades, bricks, and platelets are considered in this study. The governing equations in the form of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) had been reduced to nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) by using similarity transformation. The solver bvp4c in MATLAB software was applied to numerically solve the dimensionless governing equations towards the physical parameters which are aligned angle of magnetic field, interaction of magnetic field, mixed convection, Deborah number, volume fraction of nanoparticles, and nanoparticle shape factor. The effects of nanoparticle shapes and other relevant thermophysical parameters on fluid velocity, temperature, skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number are discussed in tables and figures. In comparison of all shapes, this study found that blade shaped nanoparticles have the highest values of skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number. The parameters

 and
and
 decrease the velocity profiles but increase the temperature profiles.
decrease the velocity profiles but increase the temperature profiles.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
2024-01-05
How to Cite
Noorehan Awang, Nurul Hidayah Ab Raji, Anis Athirah Rahim, Mohd Rijal Ilias, Sharidan Shafie, & Siti Shuhada Ishak. (2024). Nanoparticle Shape Effects of Aligned Magnetohydrodynamics Mixed Convection Flow of Jeffrey Hybrid Nanofluid over a Stretching Vertical Plate. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Mechanics, 112(1), 88–101. https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.112.1.88101
Issue
Section
Articles


























