Automated Defective Ceramic Tiles Classification using Image Processing Techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.3.355365Keywords:
Defective ceramic tiles, classification, shape features, k-Nearest NeighborAbstract
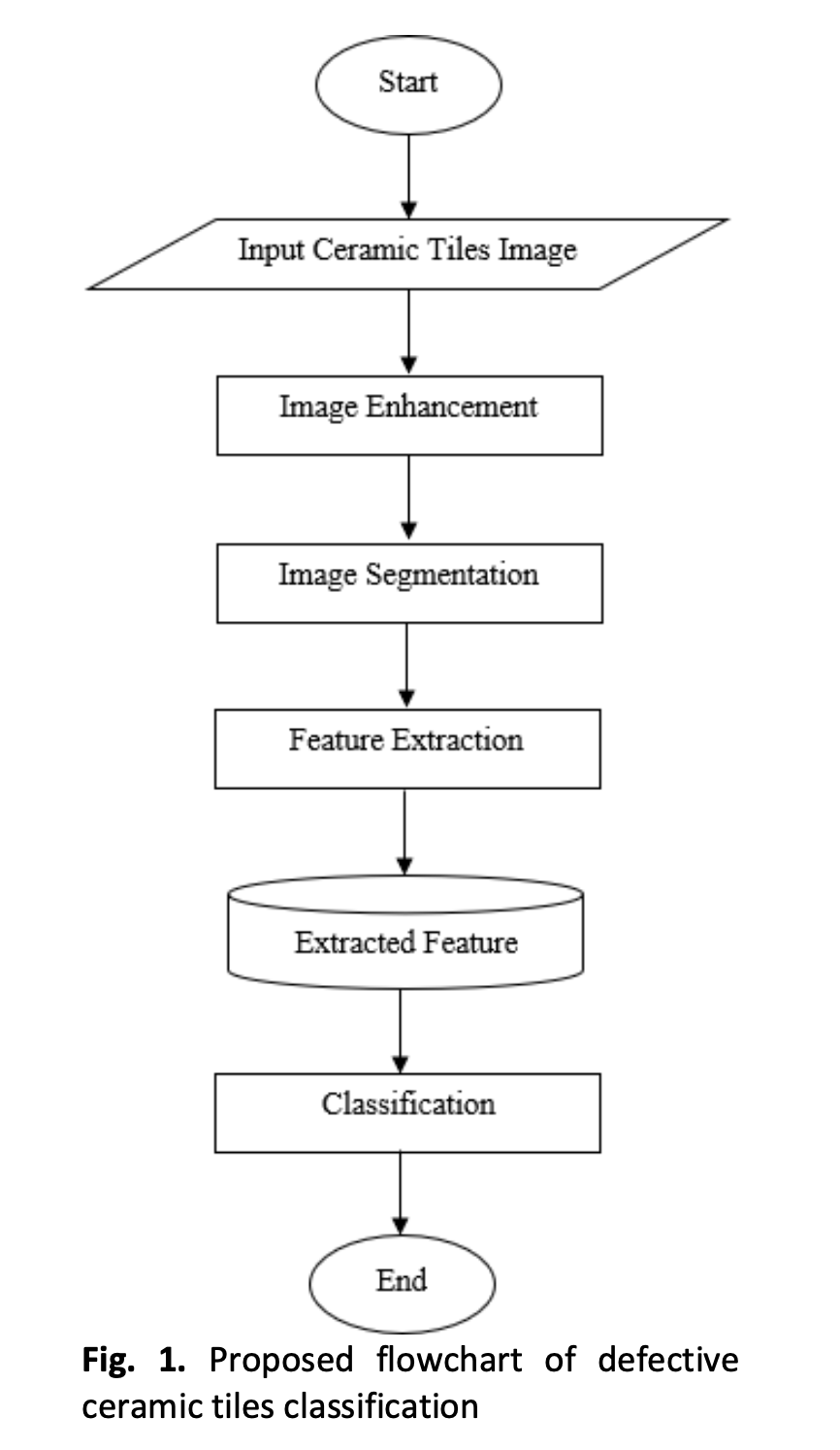
Surface quality is one of the critical issues in the ceramic tile manufacturing industry. However, there are still large amounts of ceramic tiles manufacturers who use a manual inspection process to check the quality of the ceramic tiles’ surfaces. The manual inspection is time-consuming and has low accuracy. Additionally, the slow inspection process could not keep up with the production rate. Therefore, this study presents a solution where image processing techniques are implemented to construct an automated defective ceramic tiles classification. The process consists of a few phases which include image enhancement, image segmentation, feature extraction, and classification. The input image which is the ceramic tiles image was enhanced using the histogram equalization technique. The segmentation was done using Sobel and the global thresholding technique before the feature extraction process is implemented. Three shape features of mean intensity, area, and perimeter were extracted in analyzing the characteristics of each ceramic tile defect type of crack, corner, and edge. Then, the image was classified using the K-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) technique. A confusion matrix was used to assess the performance of the k-NN classification to 150 testing images. The overall mean accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity returned good performance at 93.34%, 89.93%, and 95% respectively. Thus, it can be inferred that the proposed automated defective ceramic tiles classification using image processing techniques was successful.
Downloads