Distance of Drill-Hole Determination based on Global Estimation Variance of Coal Resources Classification
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.1.267274Keywords:
Optimum drill hole spacing, sill variogram, coal, global estimation varianceAbstract
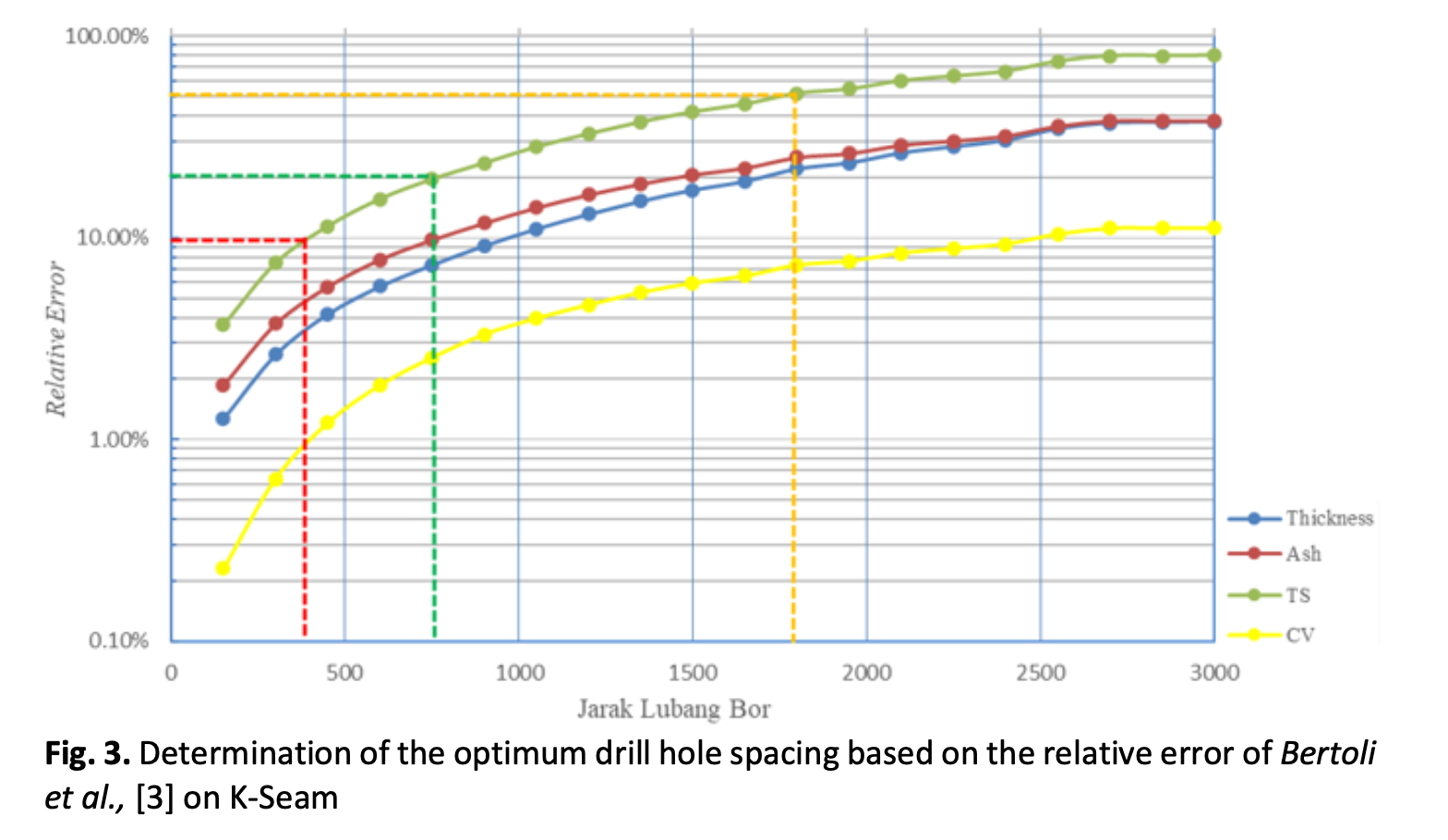
Based on SNI 5015:2019, the estimation of coal resources is based on geological conditions, as well as the distance of information points for each geological condition and resource class. PT. AMNK is a coal mining company and has now started mining. The mines are divided into three blocks, north, middle, and south. Drilling activities have been carried out in the middle block, with 66 drilling points resulting in 4 main seams namely, H seam, I seam, J seam, and K seam. The average drill hole distance is 150 m. This type of coal deposit belongs to the moderate geological group characterized by the presence of a fault in the middle block. Further analysis of optimum drill hole distances is carried out as a basis for the estimation and classification of resources, which in 2024 will be used as an exploration target for the southern block. Analysis of the optimum drill hole distance based on the "relative error" value using the GEV (Global Estimation Variance) method and the size of the sill variogram. Based on the analysis of the K seam, the optimum borehole distances were 385 m, 750 m, and 1750 m, measured, indicated, and inferred categories, respectively.