Detection of Kidney Stone and Estimation of its Size using Image Segmentation Techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.36.2.91109Keywords:
Kidney stones, Size, CT, Watershed segmentationAbstract
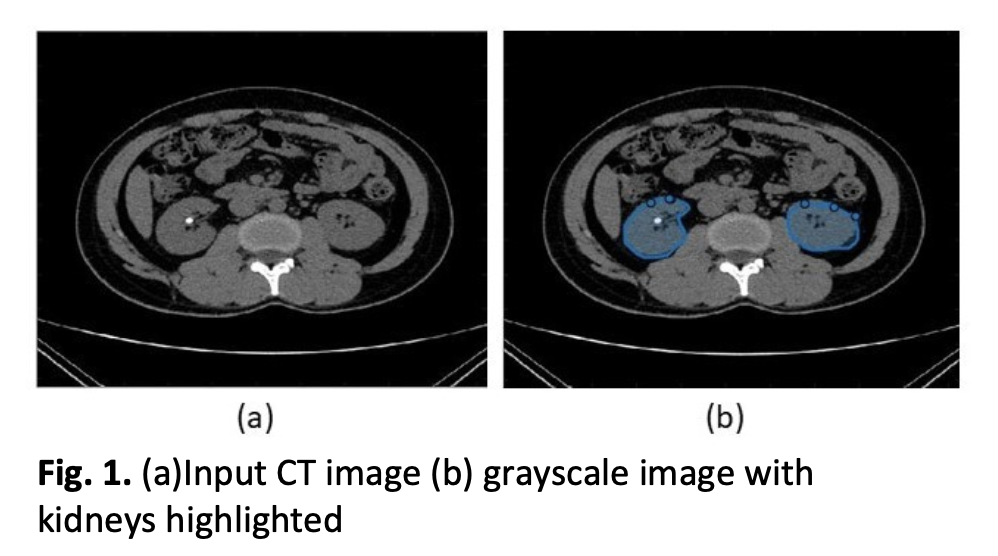
The study discusses the development of a reliable strategy for detecting and segmenting kidney stones from CT scans. Kidney stones are solid materials that can form in the kidneys due to excessive amounts of specific minerals in the urine. Severe back, side, lower abdominal, or groin discomfort, or blood in urine can indicate kidney stone presence. The current method for detection using CT scans is widely used, but it requires more precise and efficient technology due to the laborious and time-consuming manual process. The objective of this report is to propose a robust approach for kidney stone detection and segmentation, employing threshold segmentation and the watershed algorithm along with pre-and post-image processing for noise reduction. Additionally, the method estimates the size of the stone, aiding in selecting the appropriate medical procedure for stone removal. The entire process is implemented on a dataset comprising numerous kidney stone images to test and validate its accuracy and reproducibility. The system's image quality enhancement is evaluated by calculating several parameters such as SSIM, PSNR, FSIM, NCC, and NAE on the output images. To further validate the suggested method, a comparison is made with two other existing algorithms based on the mentioned evaluation criteria. The proposed strategy promises to improve the accuracy and reliability of kidney stone detection and segmentation, providing a more efficient and effective solution for medical diagnosis and treatment
Downloads