A Study of the Thermal Behavior of Some Materials Used to Prevent Corrosion in Mechanical Parts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.104.1.5564Keywords:
Thermal process, machine, inhibitor, heat transferAbstract
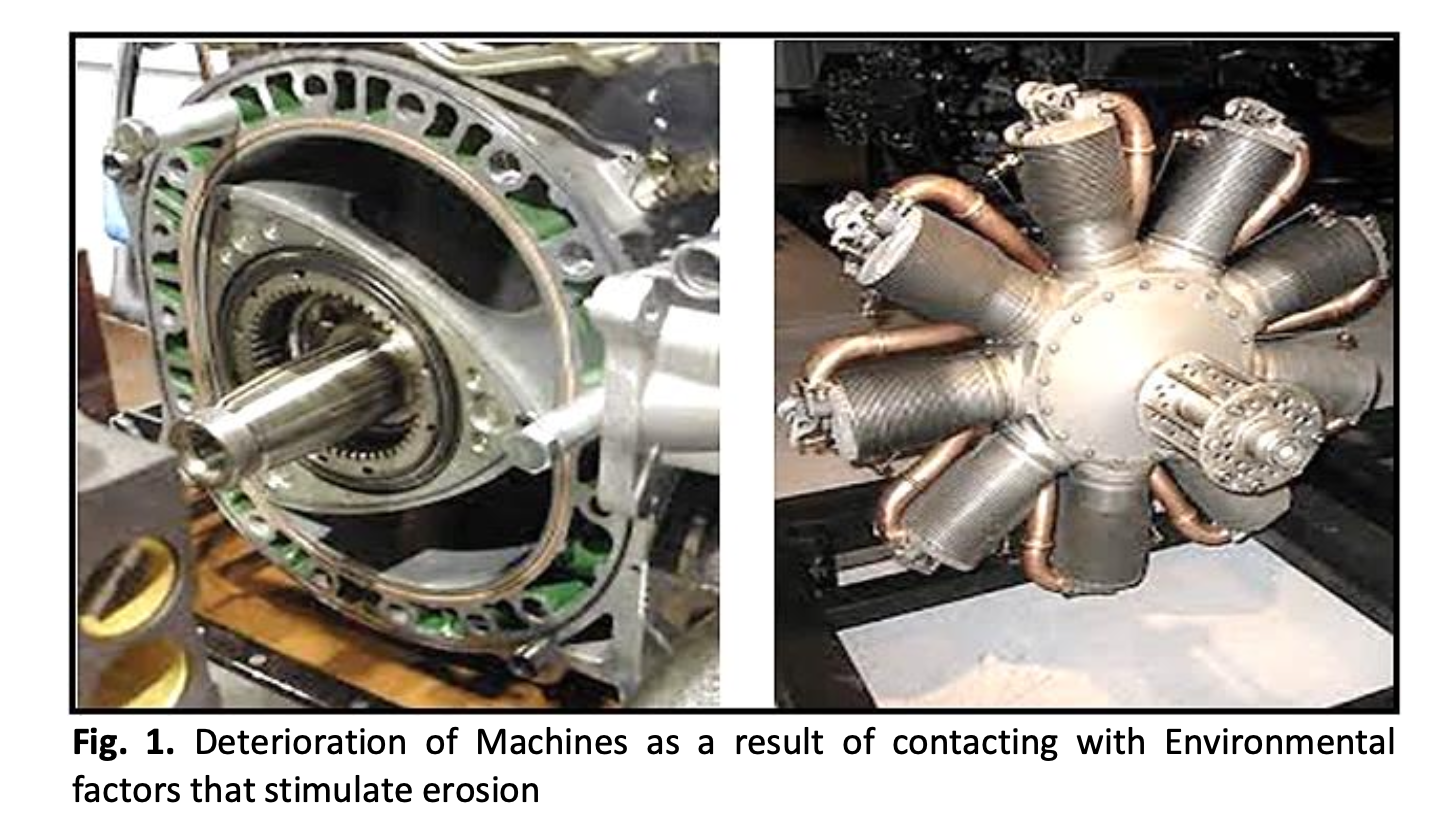
Thermal deterioration of Machines is the change in the properties of the basic material as a result of thermal reaction with its environment as a result of the presence of moisture in the bodies of machines such as the bodies of aircraft, cars, engineering equipment and related to the mechanics of the machines in the field of mechanical engineering, which is called the medium of deterioration and not as a result of a mechanical process such as friction in the machines as a result of work Continuous in these machines, according to this definition there is a possibility of corrosion not only in metals, but other materials such as concrete and containers that are in direct contact with moisture, air and environmental factors that are a catalyst for mechanical deterioration. Many researchers in mechanical engineering were interested in the thermal processes of machines, so the problem of corrosion and friction of machines and other important problems that have been studied extensively by finding engineering solutions to reduce or eliminate them. Corrosion of Machines be a limiting factor for various materials in many applications. Thus, it is necessary to have a better understanding of the deterioration processes, their prevention and reduction of the associated damage. In this research the preparation of some reagents and their use as deterioration inhibitors to reduce the deterioration process in engineering machinery by measuring the loss in weights resulting from the phenomenon of deterioration in engineering machinery. These thermal reagents were prepared as a thermal inhibitor painting, diagnosed in spectroscopic techniques, and then some thermal measurements were made to studying them as inhibitors of engineering corrosion in machines. The results appeared that the prepared reagents are good deterioration’s inhibitors due to the inhibition efficiency of the selected thermal reagents increased with increasing of concentration, and decreased with increasing of temperature.
Downloads