Blood Conveying Ferroparticle Flow on a Stagnation Point over a Stretching Sheet: Non-Newtonian Williamson Hybrid Ferrofluid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.97.2.175185Keywords:
Stagnation point flow, stretching surface, Williamson hybrid nanofluidAbstract
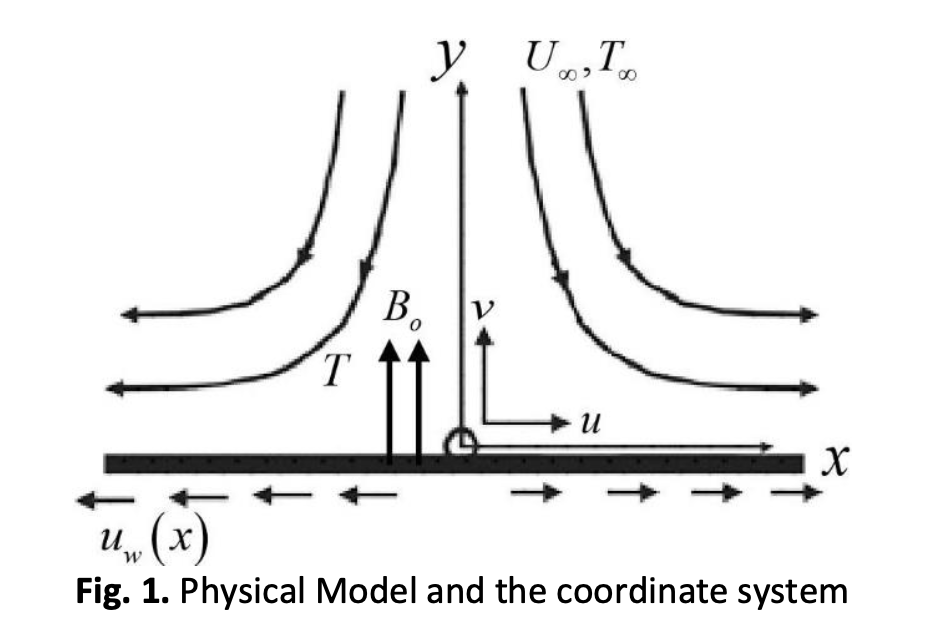
The present research investigated the characteristics of convective boundary layer flow and heat transfer of the blood carrying ferroparticle modelled known as the non-Newtonian Williamson hybrid ferrofluid. The fluid flow and the heat transfer of a stagnation point over a stretching surface are considered. The similarity transformation approach is used to reduce the partial differential equation system to an ordinary differential equation. The transformed equations are then solved numerically by Runge-Kutta-Felberg (RKF45) method in Maple software. The flow characteristic and the heat transfer of the non-Newtonian Williamson hybrid nanofluid are tested from various pertinent fluid parameters. The temperature distribution, velocity profiles, as well as variation of the Nusselt number and the skin friction coefficient are analysed and discussed. The study reveals that the non-Newtonian Williamson Hybrid ferrofluid potentially provided better performance in heat transfer capability compared to ferrofluid with the same volume of nanoparticle volume fraction.
Downloads