Numerical Boundary Layer Solution of Ferrofluid Over a Horizontal Flat Plate with Passive Control Boundary Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.125.2.180189Keywords:
Ferrofluid, flat plate, passive control boundary conditionAbstract
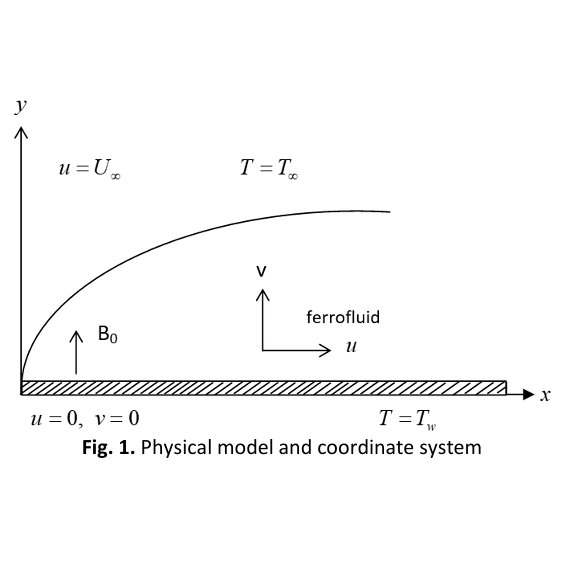
Numerical solution of ferrofluid over a flat plate is analysed in this study. An external magnetic field is applied in the transverse direction to the flat plate. For this purpose, magnetite (Fe3O4) as a ferroparticle and water as a base fluid are considered. A boundary condition is applied with the assumption that there is no nanoparticle flux at the surface. The nanoparticle volume fraction on the boundary is passive control rather than active. The governing equations which are non-linear partial differential equation are converted into linear by using similarity transformation and then are solved numerically by using Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method. The obtained results of this studied are compared to regular fluid without magnetic effect and normal boundary condition where the results show good agreement. With the numerical results, the effects of volume fraction of solid ferroparticles, magnetic parameter, Lewis number, thermophoresis parameter and Brownian motion on the velocity, temperature and volume concentration were discussed. It is found based on the results, the velocity decreases and the temperature increase with the increment of volume fraction of solid ferroparticles. Moreover, increasing thermophoresis leads to the increment in the temperature and the nanoparticle volume concentration.
Downloads