Investigation of the Effect of Different Fins Configurations on the Thermal Performance of the Radiator
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.116.1.2739Keywords:
Radiator design, heat transfer efficiency, airflow resistance and cooling effectivenessAbstract
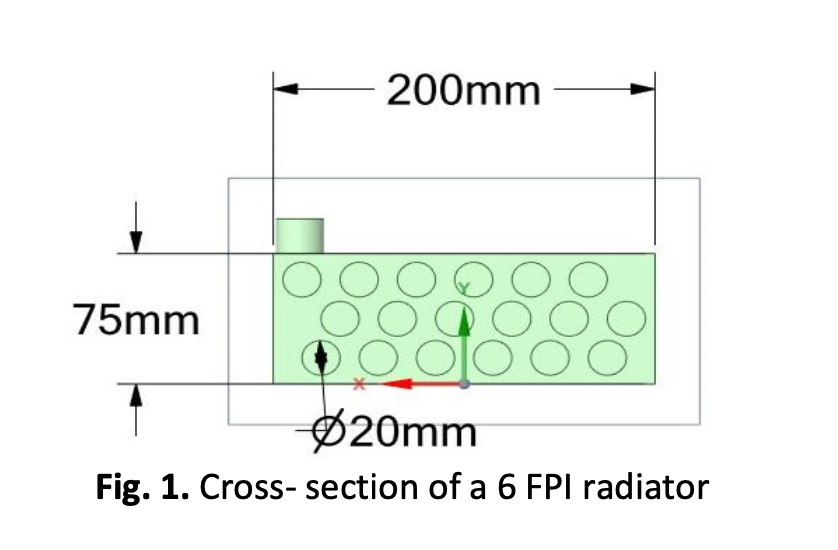
Fins play a crucial role in enhancing heat transfer in various engineering and industrial applications. In this paper, the significance of fins in heat transfer as well as the design of radiators for thermal management are discussed. Fins increase the surface area and improve convective heat transfer. Fins, however, may decrease the surface area available for heat exchange and raise airflow resistance. In order to maximize thermal performance, this study emphasizes the necessity of having a thorough understanding of the relationship between fins and tubes in radiator design. The objectives of the research are to maximize surface area for heat dissipation, assess the impact of fins on heat transfer efficiency, and examine their functions. Thermal performances of radiators with various fin densities that is, radiators with six, eight, and ten fins per inch (FPI) have been investigated using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Analysis. The ten FPI configurations, in particular, showed remarkable thermal performance, indicating its potential for applications requiring strict thermal control. Further, it is also revealed that the outlet temperature dropped as the FPI rose and proved that the FPI and outlet temperature have an inverse relationship. These findings serve as a foundational framework for future research projects and practical applications, providing essential insights into designing more effective and efficient cooling systems.
Downloads