Development of a Natural Draft Metal Biomass Cookstove for Community Kitchen
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.2.120Keywords:
Community cookstove, natural draft, input power, efficiency, fluid flow, heat transferAbstract
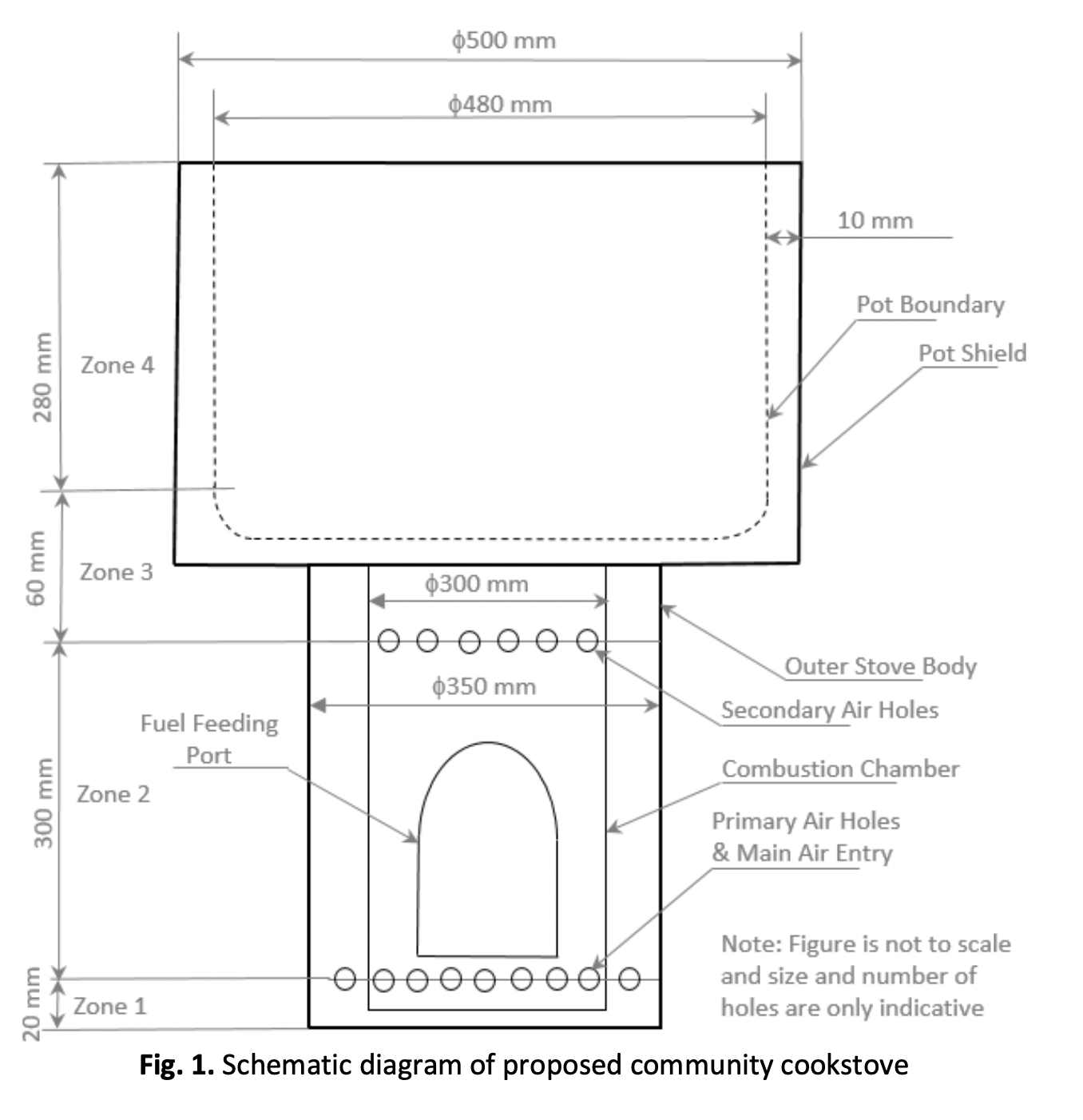
Present work reports details of the design, fabrication, and laboratory testing of a natural draft metal biomass cookstove for a community kitchen. Heat transfer and fluid flow considerations along with experimental data available in the literature are used for the design of the community cookstove. The summation of pressure drop in different sections of the cookstove is compared with the outside pressure drop for the system using buoyancy considerations. The cookstove is fabricated as per the dimensions finalized during the design stage. Laboratory testing of the cookstove is conducted according to Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) protocol. The tests are conducted under different conditions of main air hole closing viz. 0%, 25%, 75% and 100%. Each test is replicated thrice and an analysis of data is performed using a student’s t-test. The efficiency of cookstove is found to be about 42% i.e., well above the BIS limit of 25% for natural draft metal cookstove. The effect of insulation on the outer body of cookstove is studied experimentally. It is found that the efficiency enhances by about 5.3% due to insulation. The authors found that provision of primary and secondary air holes play a very important role in the performance of the cookstove. When 100% main air holes are closed, the average efficiency of the cookstove is found to be poor (27.3%) due to no supply of secondary air to the combustion chamber of the cookstove.
Downloads