Accurate Assessment Model for Solving Resistance-Temperature Equations of Platinum Thermometers in Range from -40 °C up to 660 °C
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.93.1.123135Keywords:
ITS-90, IPRT, SFE, CVD, high order polynomials, Interpolating equationsAbstract
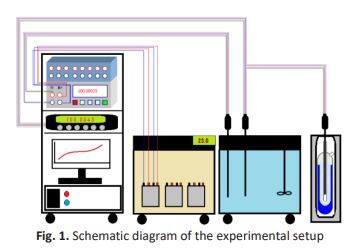
The missions of the thermal metrology laboratory are to maintain, disseminate, develop and realize the International Temperature Scale 1990 (ITS-90). One of the services that the laboratory has introduced is the routine calibration to all industrial sectors that covers almost all fields inside and outside Egypt. This work compares different interpolating equations of set of industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers (IPRTs) in the temperature range from -40 °C up to 660 °C that convert the resistance of thermometer sensing element to temperature and find the optimum method in which range applicable. The used analytical methods are Callendar–van Dusen (CVD) equation and the (4th -5th) order polynomials of resistance as a function of temperature. The study splits the ranges of investigation into lower subranges, test the significant standard error and residual for each case, and give advice to the lower level calibration laboratories that does not own primary standard about the best method used. From the results it is found that the standard fit error (SFE) for 4th order polynomial on average = 30 % compared to the CVD equation, =50 % compared to the ITS-90 deviation function and = 73% compared to the 3rd order polynomial. It is preferable to used 5th order polynomial than CVD to decrease 1 point in the calibration and reduce the cost of the calibration with nearly the same accuracy if the mathematical model is applied. The study gives advice to the end user who wants to use CVD equation by selecting the best two-calibration points above 0 °C which are 100 °C and 400 °C.
Downloads