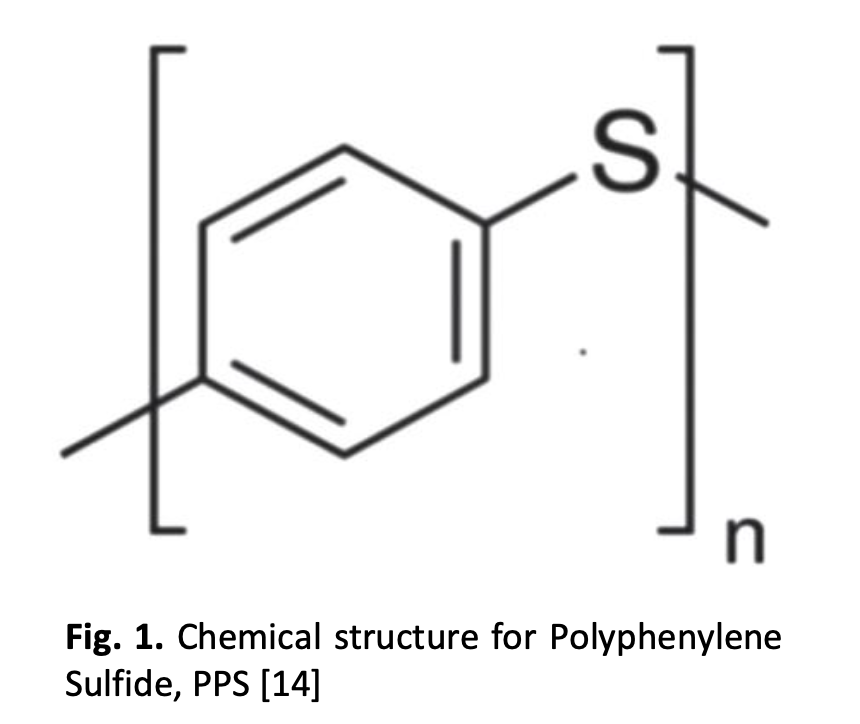
Layering Effect on Mechanical, Thermal & Physical Properties Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polyphenylene Sulfide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.98.2.128145Keywords:
CF/PPS, tensile, compression, ILSS, impact, flexural, hardness, SEM, glass transition temperature, melting temperatureAbstract
The application of thermoplastic composites (TPCs) in aircraft application is expanding. This paper presents a study of the effect of layering thickness of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polyphenylene Sulfide, CF/PPS. There are 2 thickness of plies which are 6 plies and 8 plies of 1.90 mm and 2.52 mm respectively. To update, the aircraft is now ready to shift from thermoset to thermoplastics composite materials. In parallel to the technology, mechanical, thermal and physical properties of the advanced thermoplastic materials CF/PPS are to be determined. By having towards the behavior and properties, thus the incoming material CF/PPS data could be compared to the current nominal of epoxy thermoset structural for aircraft which is benefit to the aircraft industries purpose. In this study, it was found that, for mechanical properties, Tensile Strength, Flexural Modulus as well as Vickers Hardness recorded 6 plies higher value compared to 8 plies. While, Impact Strength, Interlaminar Shear Strength, (ILSS) and Compressive Strength shown that 8 plies obtained the superior reading compared to 6 plies. For physical properties, the density of 6 plies and 8 plies recorded 1.541 and 1.547 respectively. Content as a percentage of the initial mass of fibre, (%) recorded 6 plies was 58.397% while 8 plies was 58.235 %. Fibre content as a percentage of the initial volume, (%) recorded 6 plies was 50.838% while 8 plies was 50.885%. Void content as a percentage of the initial volume, (%) recorded 6 plies was 1.678% while 8 plies was 1.268%. While, for the thermal analysis, both samples of CF/PPS have good thermal stability material in aerospace applications as the weight for both plies CF/PPS are observed as the function of temperature (high heat energy applied). Glass Transition Temperature ( was 93.75°C for 6 plies while 8 plies recorded 93.94°C. Melting Temperature, recorded 283.68°C for 6 plies whereas 283.61°C for 8 plies. The morphological analysis under Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) shows that 6 plies had a lot of fibre pull out compared to 8 plies thus agreed that impact strength was higher on 8 plies over 6 plies.
Downloads