Investigation and Analysis of Air Curtains for the Improvement of Refrigeration Energy Efficiency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.92.1.212225Keywords:
CFD, FCU, Cold room, Air curtain, Common grille, Honeycomb grilleAbstract
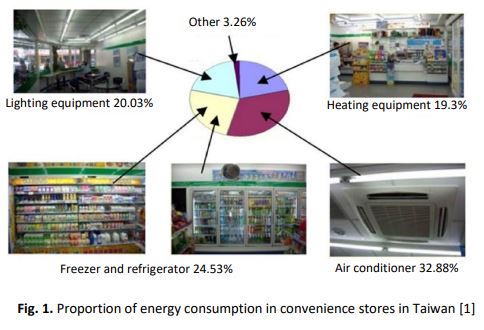
The purpose of this research is to present a warm air infiltration simulation for a cold room, considering the effects of an air curtain. At present, there exist a large number of retail businesses, operating within an industry entailing high investment and competition. Therefore, retail operators must distinguish factors that are essential to lowering their costs, one of which is energy reduction. A survey of energy consumption in stores found that most used energy is due to the cooling system. Therefore, we tested the protection of cold rooms against air inflow by conducting three simulations: 1. Without an air curtain; 2. using an air curtain having a common grille; and 3. using an air curtain with a honeycomb grille. The cold room temperature was set to 1 °C, the cold room door was 200 × 100 m2, and the air curtain was installed 5 cm above the cold room door; furthermore, the velocity of air emitted from the air curtain was 6.5 m/s. Warm air infiltration simulations were carried out using SolidWorks Flow Simulation software, in order to determine the temperature change in the cold room and the airflow direction. From the results of the comparative experiments, when using the different wind grilles, there were differences in the infiltration of warm air. The honeycomb grille reduced air turbulence in the cold room more effectively than the common grille. As a result, the temperature in the cold room was consistent, and the temperature inside the cold room was maintained 10.62% lower when using a honeycomb grille compared to a common grille.
Downloads