Effect of Reynolds Number on the Wake of a Next-Generation High-Speed Train using CFD Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.15.1.7687Keywords:
Aerodynamic, Computational fluid dynamics, Next-generation high-speed train (NG-HST), Reynolds number, Wake structureAbstract
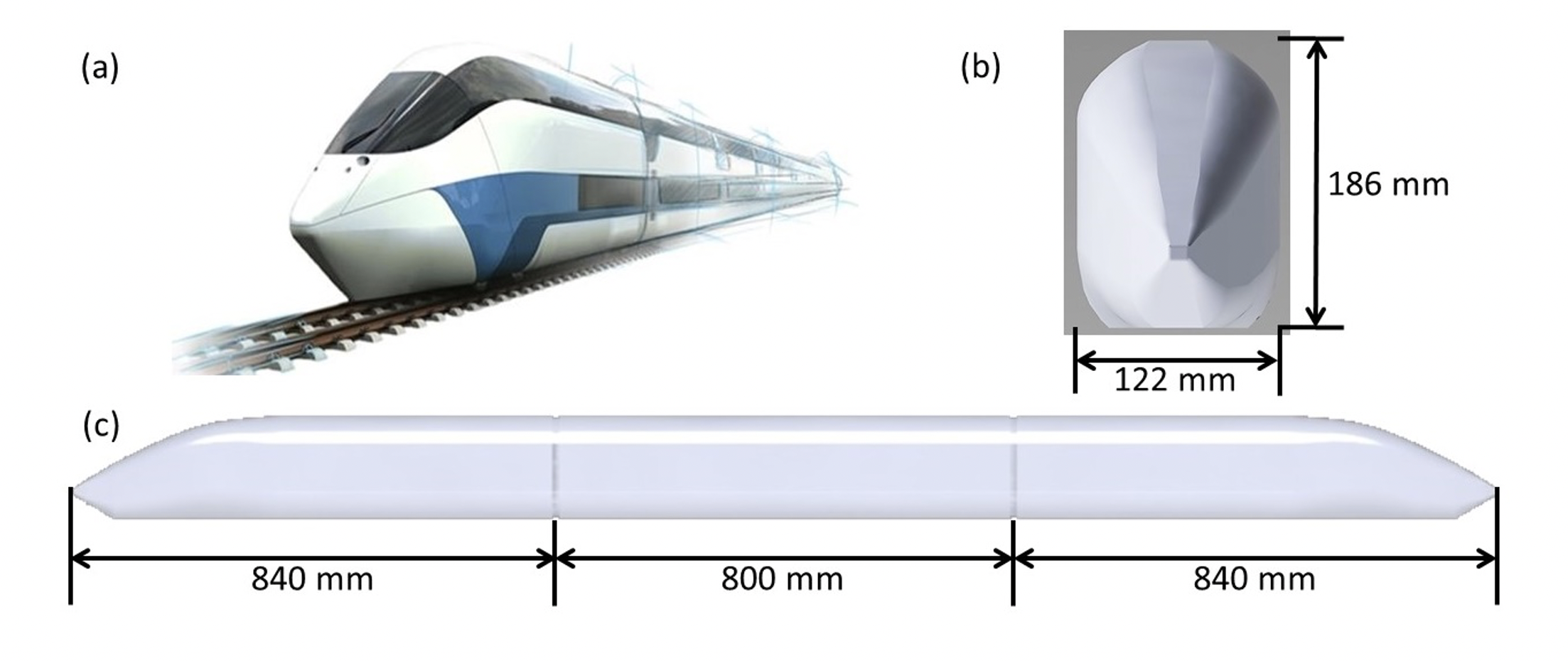
Improvement to the next-generation high-speed train (NG-HST) is ongoing particularly in achieving a higher operating speed. Consequently, the aerodynamic effect of the train will be more critical as it affects the development of a wake flow characterized by complex and unsteady structures. Although the effect of Reynolds number (Re) on aerodynamic forces is negligible, its effect on the wake of NG-HSTs is unknown. In this study, the Re ranging from 7.42 × 105 to 1.62 × 106 was used to examine the characteristics of vortex structures, streamline distributions, velocity characteristics, and pressure characteristics in the wake region of an NG-HST. The Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation (DDES) is used as the turbulence model. In addition, the simulation results were compared with the previous wind tunnel experimental data. The results indicated no significant changes in the overall wake flow structure when Re was increased. According to power spectral density analysis, increasing the Reynolds number increased the turbulence intensity of the wake which gradually dissipated as the distance from the train increased. The findings of the study could be used to better understand the flow characteristics at the wake of NG-HSTs for future development.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.