Comparison of Basic Iterative Methods Used to Solve of Heat and Fluid Flow Problems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.101.1.186191Keywords:
Iterative methods, heat and flow, CFD, ADI, SORAbstract
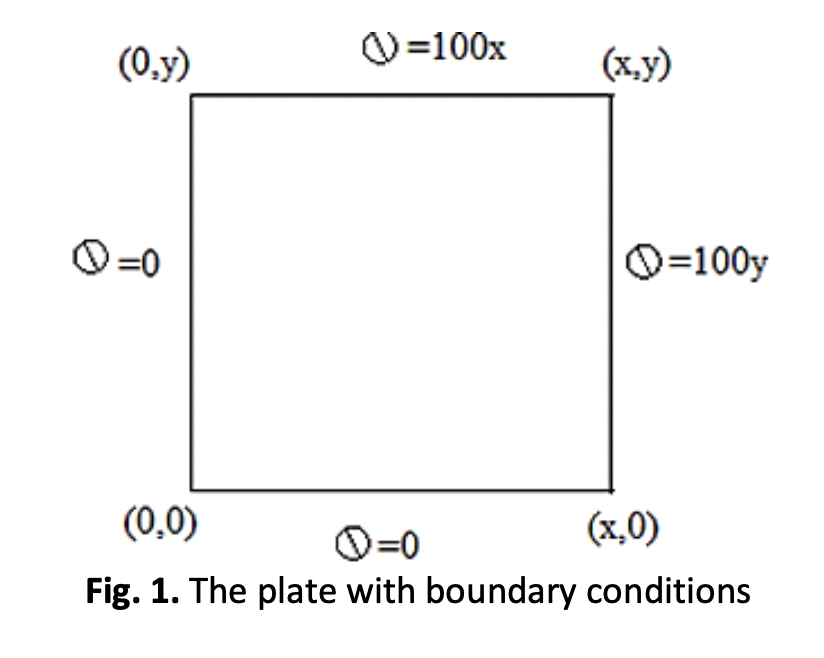
In this research, a comparison of the convergence rate of different basic methods is made in order to solve the Poisson equation, which is similar to some of the resulting equations in computational fluid mechanics. The Jacobi method, the point Gauss-Seidel method, the successive over-relaxation method (SOR), the line Gauss method (TDMA), the ADI method and Strongly Implicit (SIP) method are among the iterative approaches investigated, which are then compared to find the most optimal method. The selection criteria included the number of iterations and the time needed to reach convergence. In both selection criteria, the SIP approach has been shown to be the most efficient.
Downloads