Spray Drying Optimization for Rice Bran Protein (RBP) Powder using Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.95.1.6475Keywords:
Spray drying, rice bran protein (RBP) powder, response surface methodology (RSM)Abstract
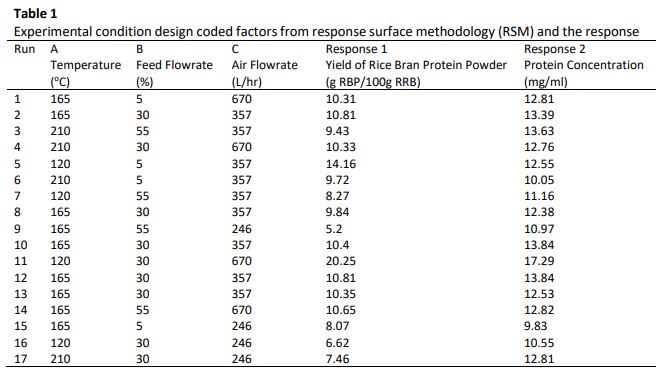
Rice bran is a by-product of the rice milling process which contain a high concentration of protein. It’s are often used as a feed cattle, fertilizer, and fuel. Its application as a source of human nutrition is rare due to high lipid concentration. This lipid concentration can be reduced through the extraction process. After the extraction process, the rice bran extract needs to be converted into powder form through a drying process for the quality preservation. In this study, spray drying is utilized as drying technique. The aims of this study were to optimize the spray drying parameter; inlet temperature, feed flowrate and air flowrate for rice bran protein (RBP) powders production. Box Behnken Design (BBD) model in response surface methodology (RSM) are utilized in this study to maximize the RBP powder yield and protein concentration. Raw rice bran (RRB) was extracted using thermal water-based extraction method before the drying process. The optimum condition suggested by the model are at the inlet temperature of 120oC, feed flowrate of 18.38% and air flowrate of 670 L/hr which produced RBP powder yield of 19.42 g RBP/100g RRB and protein concentration of 17.32 mg/ml. The model obtains in this study show a low error between the predicted value and experimental data at 1.68 % and 1.14 % for RBP powder yield and protein concentration respectively. The model can be used to evaluate the process characteristic and understanding.
Downloads