Effect of Pore Size and Hydrophobic Coating on Oil-Water Separation System for Grease Trap
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.97.1.119126Keywords:
Oil-water separation, hydrophobic coating, pore size, Pugh methodAbstract
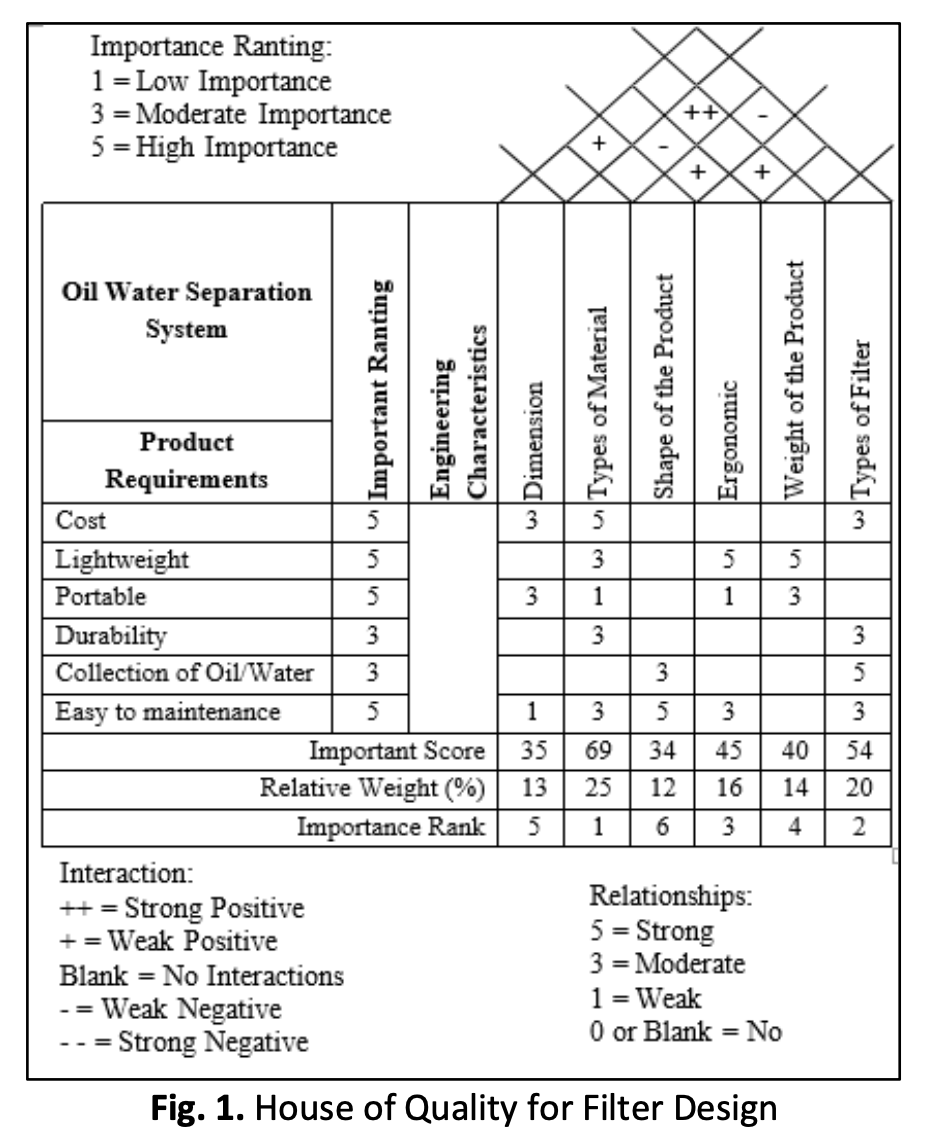
Public concern towards solidification of fat, oil, and grease (FOG) through disposed wastes into the drainage system is an unresolved issue to this day. The use of skimmer to separate oil and water form their mixture is a less comprehensive solution. This paper aimed to design the concept and fabricate oil-water separation medium, as well as to analyse the effect of different pore sizes of wire mesh and coating respectively. Water separation system is designed based on Pugh Method, while stainless steel wire mesh is used in analysing the water repellent and oil absorption characteristics. Titanium dioxide is used as coating. Surface characterization and contact angle of droplet were observed using scanning electron microscope and contact angle measurement tools. Hydrophobicity of uncoated stainless steel of wire mesh will increase if the pore size of wire mesh is decreasing in size. The more layers of coating increase the hydrophobicity of the wire mesh in increments with contact angle more than 100⁰. For the cooking oil droplet to expeditiously spread over the mesh surface and rapidly permeate through the mesh less than 1 second, showed the oleophilic nature of the mesh.
Downloads